When left unchecked, inflammation can lead to chronic conditions due to its persistent and detrimental effects on body tissues. Initially, inflammation is a natural and essential response to injuries, infections, or other challenges, aiming to remove the harmful stimuli and promote healing. However, when the inflammatory process becomes chronic, it harms healthy tissues and disrupts normal cellular functions.
Over time, this sustained immune response can lead to the accumulation of damage, tissue scarring, and oxidative stress. Chronic inflammation is strongly associated with a wide range of debilitating conditions that include cardiovascular disease, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and certain cancers.
Additionally, it can contribute to the deterioration of organ systems and the development of persistent pain, ultimately undermining overall health and well-being. Therefore, managing and resolving inflammation is crucial in preventing the progression of acute conditions into chronic and debilitating diseases.
CellStim Microcurrent Therapy is a cutting-edge approach to reducing inflammation and edema in the body. This non-invasive treatment harnesses the power of low-level electrical currents to target areas of the body affected by inflammation and edema. The microcurrents used in this therapy are extremely gentle and mimic the body’s natural electrical signals, making them well-tolerated by patients. When applied to the affected area, these microcurrents work on a cellular level, stimulating the body’s natural healing processes.


One of the key mechanisms by which CellStim Microcurrent Therapy reduces inflammation and edema is by promoting the release of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the main energy molecule required for cellular regeneration. Increased ATP production leads to improved cellular function and can enhance the rate of tissue repair. Additionally, the therapy helps to improve blood circulation and lymphatic drainage, which aids in the removal of excess fluid and toxins from the affected area. By enhancing these physiological processes, CellStim Microcurrent Therapy effectively reduces swelling and inflammation, providing patients with relief from pain and discomfort. This innovative approach to managing inflammation and edema is particularly valuable for individuals seeking non-pharmacological and non-surgical alternatives for their conditions.

The CellStim waveform is designed to replicate the body’s natural electrical signals, with a distinctive waveform characterized by a fast rise-time and exponential fall-time. This waveform closely mimics the way in which our own physiological signals function, making it an ideal choice for therapeutic applications. The fast rise-time is critical for initiating the desired cellular responses promptly, while the exponential fall-time ensures that the electrical stimulation is gentle and closely resembles the body’s natural electrical decay patterns. This design feature helps to prevent any discomfort or adverse reactions that might occur with abrupt changes in electrical signal intensity.
Waveform Exponential Fall-Time
The CellStim waveform’s unique exponential decay characteristic expedites healing processes by distinctly modulating sodium-potassium levels during its decay phase, a feature that sets it apart from conventional constant current square waves. This tailored approach aligns more closely with the body’s natural bio-electrical dynamics, as cells often exhibit varying sodium-potassium concentration gradients during signaling. By simulating these natural fluctuations, the CellStim waveform promotes cellular membrane potential restoration, which plays a vital role in various cellular functions, including activation of ion channels and transporters. This dynamic modulation enhances the exchange of essential ions, facilitates the removal of waste products, and improves overall cellular communication and nutrient uptake, contributing to a more efficient and targeted healing response. The result is a therapy that accelerates recovery processes and provides a more biologically compatible and effective means of reducing inflammation /edema, promoting tissue repair and well-being.
Anti-Acclimatization Waveform
CellStim’s automatic frequency changing waveform technology represents a cutting-edge solution to mitigate acclimatization issues in a variety of medical conditions. By dynamically altering the waveform’s frequency, CellStim ensures that cells, tissues, or biological systems exposed to the stimulus do not adapt or become less responsive during a treatment application, preserving the effectiveness of the treatment. This innovation holds significant promise in areas like neuromodulation, where consistent and adjustable stimulation is vital and where precise control over cell responses is paramount. CellStim’s groundbreaking approach contributes to improved patient outcomes in the challenge of acclimatization in a dynamic and adaptive manner.
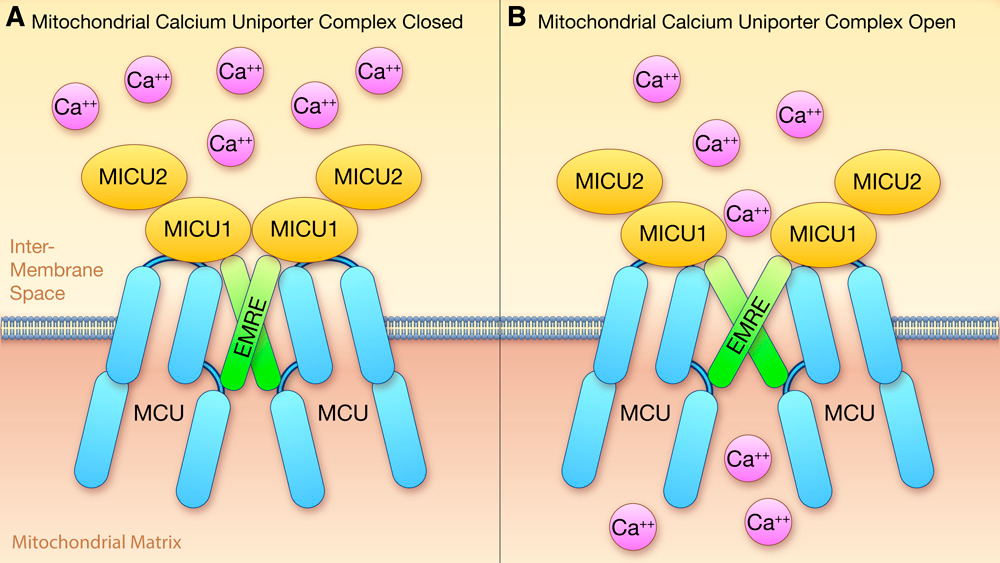
The CellStim waveform’s ability to open second messenger mitochondrial Ca ion channels is a significant breakthrough in the field of microcurrent therapy. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells and play a central role in energy production. The controlled opening of Ca ion channels in the mitochondria through the CellStim waveform enhances cellular respiration and ATP production. This not only accelerates tissue repair and healing but also optimizes cellular function. By leveraging this advanced technology, CellStim offers a unique approach to promoting health and well-being, harnessing the body’s own signaling pathways to provide targeted, effective, and non-invasive therapy for various conditions.
CellStim CS400T Treatment Parameters:
Frequency set to 0.3 Hz
Current intensity set to 300 uA or sub-threshold
Biphasic waveform (Triphasic Switch center position)
Treatment duration: 60 minutes per day
Pad placement
Place electrode pads 2-3 inches apart over area of injury

References
Anti-inflammatory Effects of Low-frequency Stimulator using Superposition of Alternating Microcurrent Wave in the Animal Models (Jun 2021)
https://www.bslonline.org/journal/view.html?doi=10.15616/BSL.2021.27.2.99
This present study measured the recovery of inflammation caused by viral infection of the sinuses during 4 weeks of microcurrent treatment. This microcurrent was found to be associated with a statistically significant decrease in epithelial cell proliferation and infiltration of inflammatory cells within the nasal epithelial tissue over time of treatment. Similarly, microcurrent has been associated with a tendency to decrease secretion of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, MIP-2 and IFN-γ). Importantly, this is the first report of a bio-electronic device capable of producing anti-inflammatory effects in addition to the pain-free treatment commonly associated with neuro-modulatory management of pain. The study of the tissue healing mechanisms of microcurrents has been known since the discovery of bioelectricity in tissue damage (Cheng et al., 1982). The microcurrent creates a cell membrane potential difference through the sensitive channels of cells inside the human body, opens the cell membrane and moves Ca2+ ions into the cell membrane. Through chemical processes by transferred Ca2+ ions, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and protein production are increased. Based on these facts, a supply of electrical energy at the cellular level that can create a cell membrane potential difference can achieve a wound healing effect 9. When tissues are damaged, the immune system affects cellular potential, and the damaged area has an overall increased resistance to the surrounding area (Becker, 1985).
[1] Effects of electrical stimulation on skin surface (Feb 2021)
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10409-020-01026-2
Role of Mitochondrial Calcium and the Permeability Transition Pore in Regulating Cell Death (Jan 2020)
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316306
Mitochondria are well established as bioenergetic hubs for generating ATP but have also been shown to regulate cell death pathways. Indeed many of the same signals used to regulate metabolism and ATP production, such as calcium and reactive oxygen species, are also key regulators of mitochondrial cell death pathways.
The effects of electric currents on ATP generation, protein synthesis, and membrane transport of rat skin
The effects on ATP production can be explained by proton movements on the basis of the chemiosmotic theory of Mitchell, while the transport functions are controlled by modification in the electrical gradients across the membranes.
